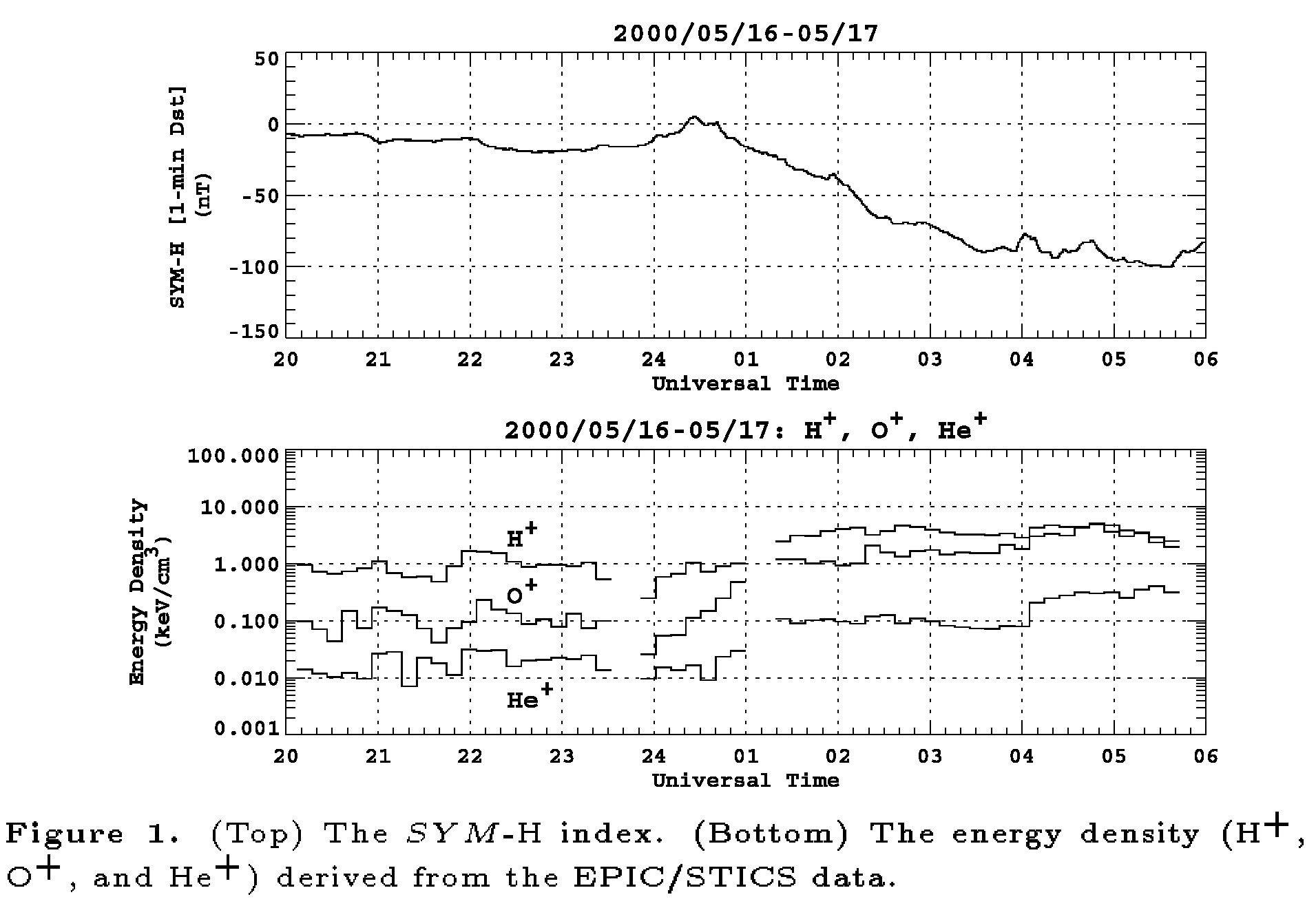
磁気嵐主相におけるプラズマシートイオン組成の変化
磁気嵐主相におけるプラズマシートイオン組成の変化
*能勢 正仁[1], K. Takahashi[2], S. Ohtani[2]
A. T. Y. Lui[2], R. W. McEntire[2]
D. J. Williams[2], S. P. Christon[3]
The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory[2]
Focused Analysis and Research[3]
Change of the plasma sheet ion composition during magnetic storm development
*Masahito Nose[1]
,K. Takahashi [2],S. Ohtani [2]
A. T. Y. Lui [2],R. W. McEntire [2],D. J. Williams [2]
S. P. Christon [3]
Data Analysis Center for Geomagnetism and Space Magnetism, Kyoto University[1]
The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory[2]
Focused Analysis and Research[3]
In the present study we investigate the energy density of H+, He+, and O+ ions in the plasma sheet during the main phase of magnetic storms, using energetic (9-210 keV) particle flux data obtained by the EPIC instrument on the Geotail spacecraft. The focus of the study is placed on how the O+/H+ and He+/H+ energy density ratios change as the Dst index decreases. We also investigate the effect of storm-time substorms on the energy density ratios. We will discuss what mechanisms are responsible for change of the energetic ion composition in the plasma sheet during magnetic storms.
磁気嵐の時には、外部リングカレント(L=5-7)領域のエネルギー
イオン(20-200keV)の組成が大きく変化する。静穏時には、H+ イオンが主成分をなすが、磁気嵐が起こると、電離層起源イオン、
とりわけO+イオンの割合が増加すると言われてきた。近年の
ジオテイル衛星の観測から、この外部リングカレント領域の
エネルギーイオン組成の変化は、地球近傍プラズマシートでの
イオン組成変化を反映していることが分かった。しかし、なぜ
O+イオンがプラズマシート中でリングカレントのエネルギーまで
加速されるかは、よく分かっていない。
この研究では、ジオテイル衛星搭載のEPIC観測器で計測された
エネルギーイオンフラックス(9-210keV)のデータを解析して、
プラズマシートにおけるH+、He+、O+イオンのエネルギー密度が
磁気嵐主相でどのように変化するのかを調べる。そして、どの
ようなメカニズムが、エネルギーイオンの組成変化に重要な
役割を果たしているのかについて議論する。また、磁気嵐時の
サブストームは、イオン組成の変化に影響を及ぼすのかについて
も焦点をあてる。