Development of Superconducting Tunnel Junctions for EUV Detectors
*Yoshiyuki Takizawa[1]
,Tokihiro Ikeda [1],Takayuki Oku [1]
Chiko Otani [1],Kazuhiko Kawai [1],Hiromi Sato [1]
Hirohiko M Shimizu [1],Hiromasa Miyasaka [1]
Hiroshi Watanabe [1]
RIKEN[1]
Superconducting tunnel junctions (STJs) have the potential for
good phot on detectors which can have energy resoluti on and
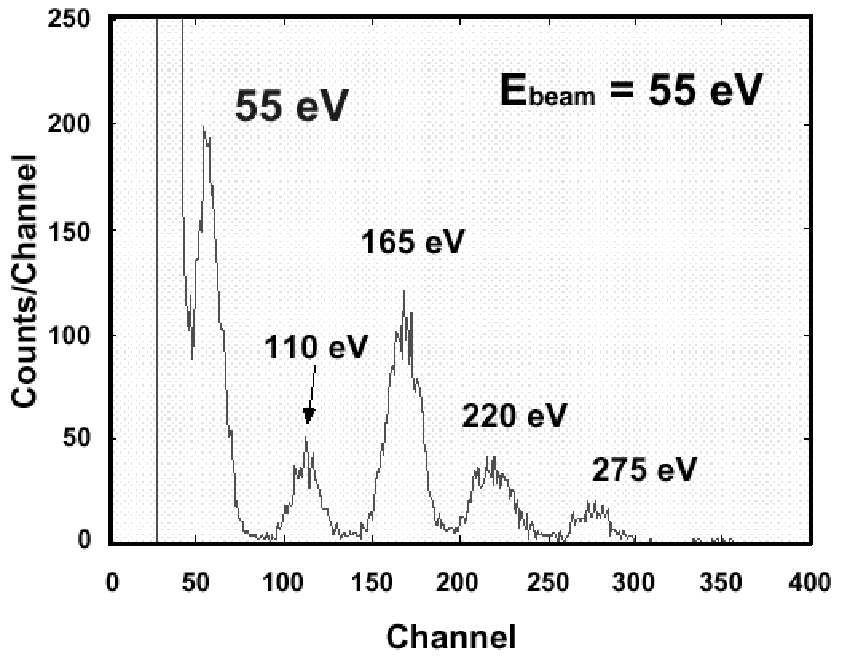
a high photon counting rate. We have a chieved the energy resolution
of FWHM=18 eV (including th e external noise of 17 eV) for 55
eV EUV photons with a 100 x 100 um^2 STJ.
Superconducting tunnel junctions (STJs) have the potential for good photon detectors which can have energy resoluti on and a high photon counting rate. The basic physical pri nciple underlying the STJs is that an absorbed photon pro duces quasipar ticles that are then recorded as a charge pul se. STJs have good performance for soft X-ray and extre me ultraviolet (EUV), because materials of STJs have high absorptance below 1 keV. We are developing an energy-di spersive detector for EUV radiation using ST Js with Al trapping layers. We have evaluated the performance of the detector for EUV photons using the Synchrotron Facility at KEK-PF in Tsukuba, Japan. We have a chieved the energ y resolution of FWHM=18 eV (including th e external nois e of 17 eV) for 55 eV EUV photons with a 100 x 100 um^2 STJ. In this presentation, we will present and discuss the details of the junction design, our experiments and the results.
Development of Superconducting Tunnel Junctions for EUV Detectors